中国沙漠 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 96-108.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2025.00197
收稿日期:2025-05-23
修回日期:2025-07-10
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-08-18
通讯作者:
左小安
作者简介:张晶(1988—),女,甘肃榆中人,博士,主要从事生态政策、恢复生态学等方面的研究。E-mail: zhangj@llas.ac.cn
基金资助:
Jing Zhang( ), Xiaoan Zuo(
), Xiaoan Zuo( ), Peng Lv
), Peng Lv
Received:2025-05-23
Revised:2025-07-10
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-08-18
Contact:
Xiaoan Zuo
摘要:
降雨变化与氮添加显著影响半干旱区草地生态系统的结构与功能。为揭示二者对植被群落特征、土壤理化性质的影响及其对生物量的调控机制,本研究以科尔沁沙地沙质草地为对象,于2021年和2022年开展野外模拟控制试验,设置4种降雨处理:5—9月减雨60%(-60%)、增雨60%(+60%);5—6月减雨100%(-60d)、增雨100%(+60d)与氮添加处理(全年施氮总量为20 g·m-²),系统分析生长季内生态因子的响应规律。结果表明:降雨变化和氮添加在不同年份对群落结构、多样性指数及土壤理化性质产生了显著影响。减雨处理显著降低植被盖度,增加物种密度,且生长季前期的极端干旱(-60d)对地上生物量的抑制作用强于整个生长季减雨(-60%)。氮添加显著提高植被盖度和地上/地下生物量,但同时降低了物种丰富度,强化了资源竞争,促使优势种扩张,进而导致群落多样性下降、均匀度降低、优势度上升。在土壤方面,氮添加引发土壤酸化,导致黏粉粒下降。干旱条件下,具耐旱或避旱特性、个体较大的优势种逐步占据主导地位,推动群落生物量提升;而氮添加则通过增强植被盖度与高度进一步促进生物量积累。降雨变化与氮添加共同重塑了植被结构、资源竞争格局与土壤理化过程,深刻影响了半干旱沙质草地生物量的形成机制。
中图分类号:
张晶, 左小安, 吕朋. 降雨量和土壤氮含量对半干旱沙质草地生产力的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 96-108.
Jing Zhang, Xiaoan Zuo, Peng Lv. Effects of soil nitrogen content and rainfall on vegetation productivity in semi-arid sandy grassland[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(4): 96-108.
| 月份 | 2021年 | 2022年 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | -60d | +60d | -60% | +60% | CK | -60d | +60d | -60% | +60% | ||
| 合计 | 316.6 | 227.2 | 406.0 | 126.64 | 506.56 | 380.00 | 191.6 | 568.4 | 152.00 | 608.00 | |
| 5 | 8.4 | 0.0 | 16.8 | 3.36 | 13.44 | 15.40 | 0.0 | 30.8 | 6.16 | 24.64 | |
| 6 | 81.0 | 0.0 | 162.0 | 32.40 | 129.60 | 173.00 | 0.0 | 346.0 | 69.20 | 276.80 | |
| 7 | 159.0 | 159.0 | 159.0 | 63.60 | 254.40 | 50.40 | 50.4 | 50.4 | 20.16 | 80.64 | |
| 8 | 68.2 | 68.2 | 68.2 | 27.28 | 109.12 | 141.20 | 141.2 | 141.2 | 56.48 | 225.92 | |
表1 2021、2022年研究区生长季降雨
Tabel 1 Rainfall during the growing season in the study area in 2021 and 2022
| 月份 | 2021年 | 2022年 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | -60d | +60d | -60% | +60% | CK | -60d | +60d | -60% | +60% | ||
| 合计 | 316.6 | 227.2 | 406.0 | 126.64 | 506.56 | 380.00 | 191.6 | 568.4 | 152.00 | 608.00 | |
| 5 | 8.4 | 0.0 | 16.8 | 3.36 | 13.44 | 15.40 | 0.0 | 30.8 | 6.16 | 24.64 | |
| 6 | 81.0 | 0.0 | 162.0 | 32.40 | 129.60 | 173.00 | 0.0 | 346.0 | 69.20 | 276.80 | |
| 7 | 159.0 | 159.0 | 159.0 | 63.60 | 254.40 | 50.40 | 50.4 | 50.4 | 20.16 | 80.64 | |
| 8 | 68.2 | 68.2 | 68.2 | 27.28 | 109.12 | 141.20 | 141.2 | 141.2 | 56.48 | 225.92 | |
| 处理 | 盖度 | 物种丰富度 | 密度 | AGB | BGB | 凋落物量 | H | D | J |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降雨 | 13.28** | 2.14 | 2.35 | 3.67* | 3.61* | 7.29** | 0.84 | 1.29 | 1.91 |
| 加氮 | 25.46** | 10.20** | 1.98 | 21.98** | 10.63** | 2.02 | 23.29** | 29.26** | 18.70** |
| 年 | 27.67** | 19.18** | 18.61** | 16.01** | 18.15** | 3.15 | 17.39** | 12.85** | 2.02 |
| 降雨×加氮 | 1.90 | 1.44 | 1.72 | 2.22 | 1.87 | 1.02 | 1.03 | 1.46 | 2.82 |
| 降雨×年 | 1.52 | 0.66 | 3.74* | 0.41 | 0.91 | 1.19 | 1.39 | 1.44 | 2.40 |
| 加氮×年 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.53 | 3.05 | 0.70 | 0.18 | 0.85 | 2.37 | 1.61 |
| 降雨×加氮×年 | 0.33 | 0.39 | 1.06 | 0.24 | 0.39 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.44 | 0.56 |
表2 降雨变化和氮添加影响下沙质草地植物群落特征的方差分析
Table 2 Analysis of variance of plant community characteristics in sandy grassland under the effects of rainfall variation and nitrogen addition
| 处理 | 盖度 | 物种丰富度 | 密度 | AGB | BGB | 凋落物量 | H | D | J |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降雨 | 13.28** | 2.14 | 2.35 | 3.67* | 3.61* | 7.29** | 0.84 | 1.29 | 1.91 |
| 加氮 | 25.46** | 10.20** | 1.98 | 21.98** | 10.63** | 2.02 | 23.29** | 29.26** | 18.70** |
| 年 | 27.67** | 19.18** | 18.61** | 16.01** | 18.15** | 3.15 | 17.39** | 12.85** | 2.02 |
| 降雨×加氮 | 1.90 | 1.44 | 1.72 | 2.22 | 1.87 | 1.02 | 1.03 | 1.46 | 2.82 |
| 降雨×年 | 1.52 | 0.66 | 3.74* | 0.41 | 0.91 | 1.19 | 1.39 | 1.44 | 2.40 |
| 加氮×年 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.53 | 3.05 | 0.70 | 0.18 | 0.85 | 2.37 | 1.61 |
| 降雨×加氮×年 | 0.33 | 0.39 | 1.06 | 0.24 | 0.39 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.44 | 0.56 |
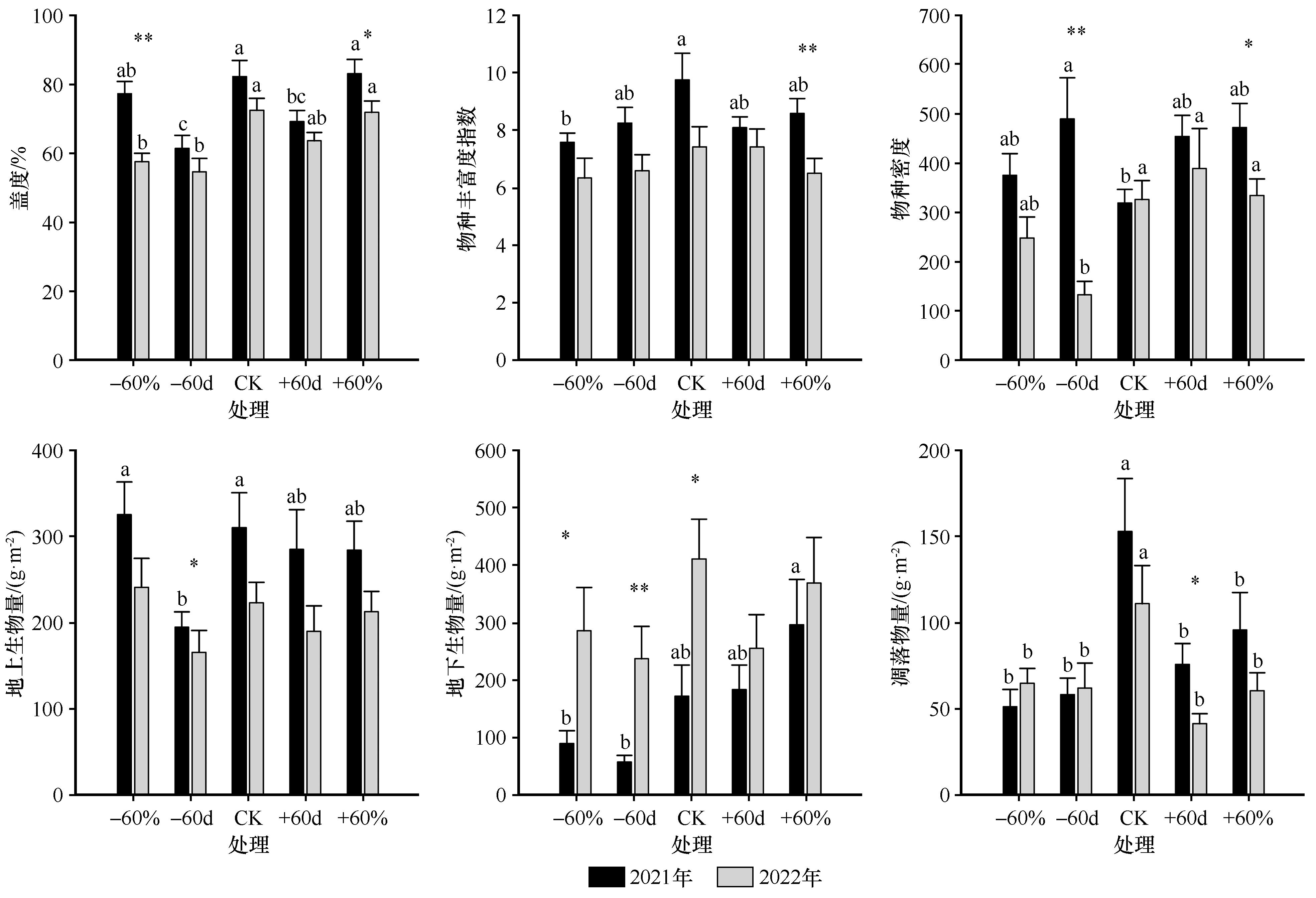
图1 降雨变化对沙质草地植被特征的影响注:-60d,5—6月减雨100%;+60d,5—6月增雨100%;-60%,5—9月减雨60%;+60%,5—9月增雨60%。不同小写字母表示同一年度不同处理间具有显著差异(P<0.05),*表示同一处理下不同年际间具有显著差异(P<0.05),**表示同一处理下不同年际间具有极显著差异(P<0.01)
Fig.1 Effects of rainfall variation on vegetation characteristics in sandy grassland
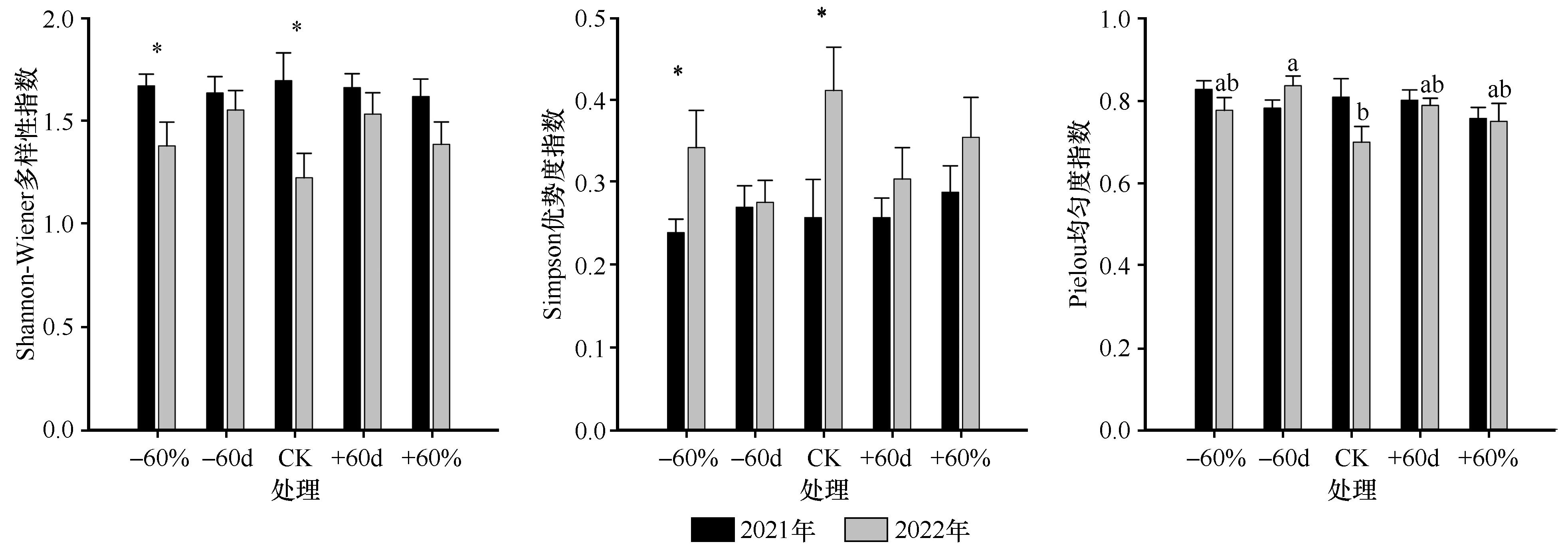
图2 降雨变化对沙质草地植被多样性指数的影响注:-60d,5—6月减雨100%;+60d,5—6月增雨100%;-60%,5—9月减雨60%;+60%,5—9月增雨60%。不同小写字母表示同一年度不同处理间具有显著差异(P<0.05),*表示同一处理下不同年际间具有显著差异(P<0.05),**表示同一处理下不同年际间具有极显著差异(P<0.01)
Fig.2 Effects of rainfall variation on vegetation diversity indices in sandy grassland
| 处理 | 土壤含水量 | pH | 电导率 | 容重 | 黏粉粒 | 土壤碳 | 土壤氮 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降雨 | 2.44 | 0.21 | 0.82 | 2.36 | 0.68 | 0.57 | 0.53 |
| 加氮 | 0.97 | 59.35** | 1.75 | 0.55 | 4.96* | 0.13 | 3.11 |
| 年 | 20.38** | 45.80** | 9.60** | 0.27 | 10.81** | 5.77* | 10.09** |
| 降雨×加氮 | 0.78 | 1.42 | 0.28 | 1.97 | 0.34 | 0.39 | 0.31 |
| 降雨×年 | 0.99 | 1.20 | 0.96 | 1.72 | 2.41 | 0.55 | 0.60 |
| 加氮×年 | 0.03 | 4.36* | 2.17 | 1.89 | 2.16 | 0.07 | 0.04 |
| 降雨×加氮×年 | 1.26 | 0.80 | 0.54 | 0.58 | 0.74 | 0.22 | 0.05 |
表3 降雨变化和氮添加影响下沙质草地土壤理化性质的方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance of soil physicochemical properties in sandy grassland under the effects of rainfall variation and nitrogen addition
| 处理 | 土壤含水量 | pH | 电导率 | 容重 | 黏粉粒 | 土壤碳 | 土壤氮 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降雨 | 2.44 | 0.21 | 0.82 | 2.36 | 0.68 | 0.57 | 0.53 |
| 加氮 | 0.97 | 59.35** | 1.75 | 0.55 | 4.96* | 0.13 | 3.11 |
| 年 | 20.38** | 45.80** | 9.60** | 0.27 | 10.81** | 5.77* | 10.09** |
| 降雨×加氮 | 0.78 | 1.42 | 0.28 | 1.97 | 0.34 | 0.39 | 0.31 |
| 降雨×年 | 0.99 | 1.20 | 0.96 | 1.72 | 2.41 | 0.55 | 0.60 |
| 加氮×年 | 0.03 | 4.36* | 2.17 | 1.89 | 2.16 | 0.07 | 0.04 |
| 降雨×加氮×年 | 1.26 | 0.80 | 0.54 | 0.58 | 0.74 | 0.22 | 0.05 |
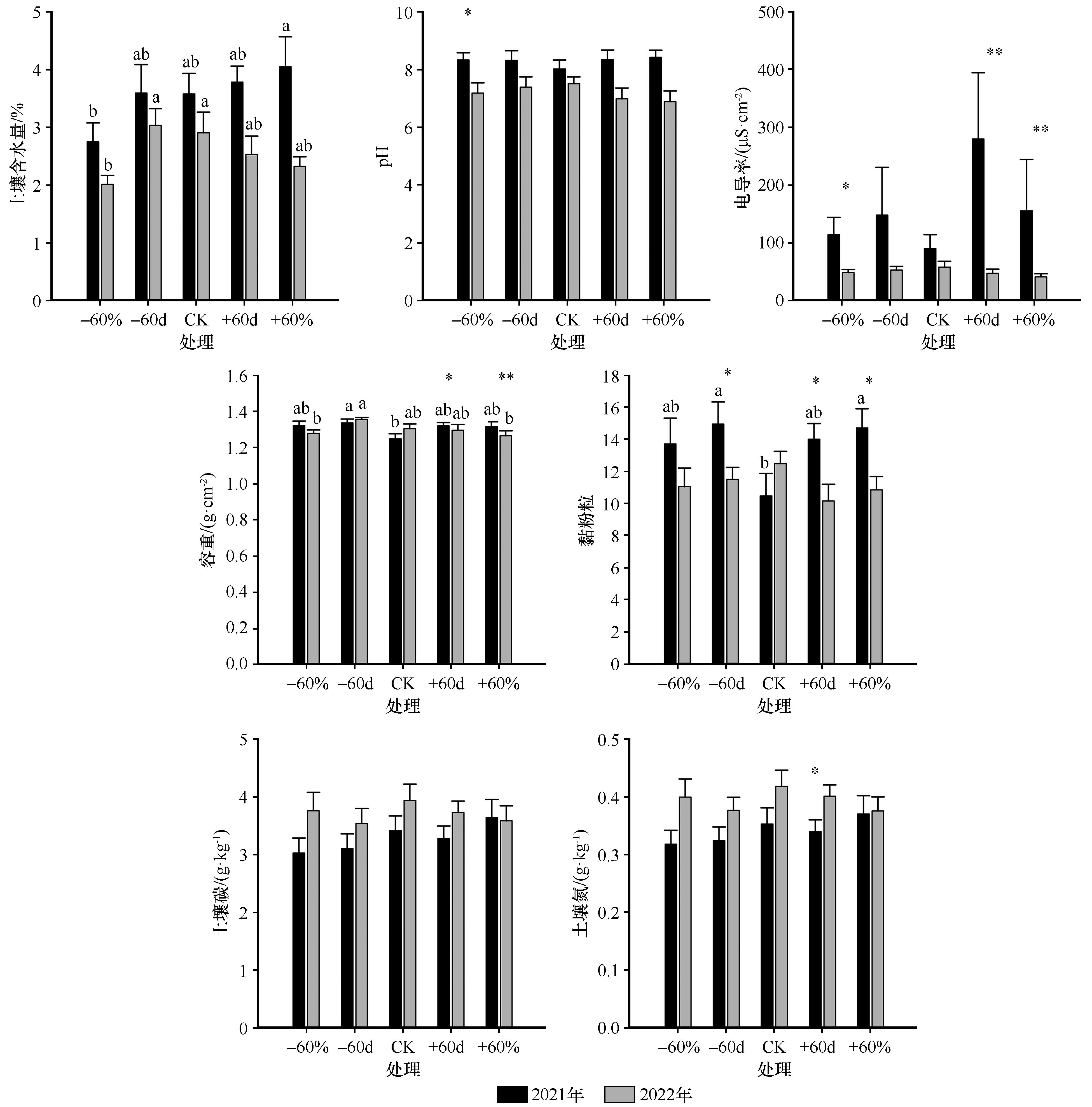
图3 降雨变化对沙质草地土壤理化性质的影响注:-60d,5—6月减雨100%;+60d,5—6月增雨100%;-60%,5—9月减雨60%;+60%,5—9月增雨60%。不同小写字母表示同一年度不同处理间具有显著差异(P<0.05),*表示同一处理下不同年际间具有显著差异(P<0.05),**表示同一处理下不同年际间具有极显著差异(P<0.01)
Fig.3 Effects of rainfall variation on soil physicochemical properties in sandy grassland
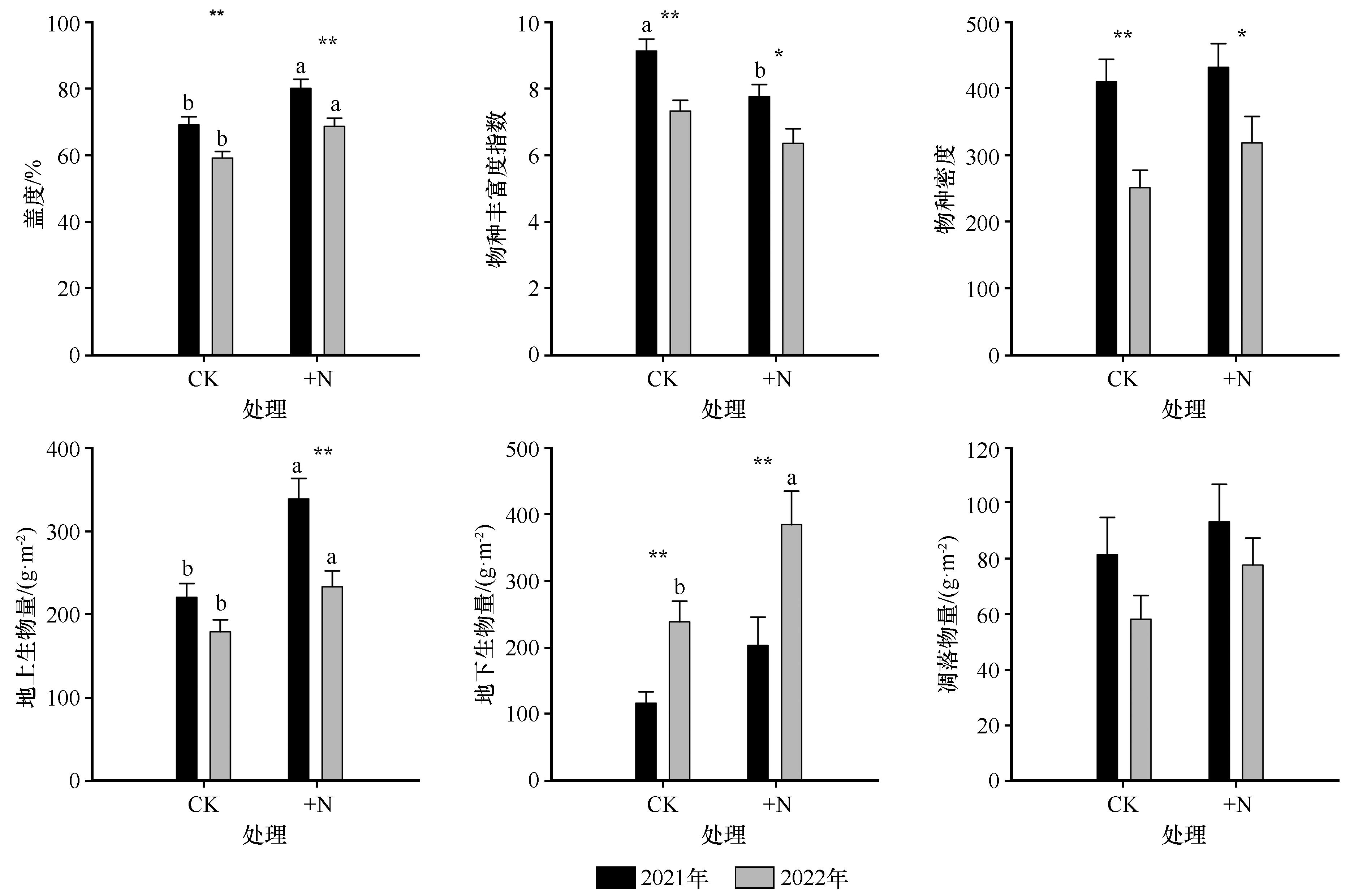
图4 氮添加对沙质草地植被特征的影响注:CK,未添加氮;+N,添加氮素。不同小写字母表示同一年度不同处理间具有显著差异(P<0.05),*表示同一处理下不同年际间具有显著差异(P<0.05),**表示同一处理下不同年际间具有极显著差异(P<0.01)
Fig.4 Effects of nitrogen addition on vegetation characteristics in sandy grassland
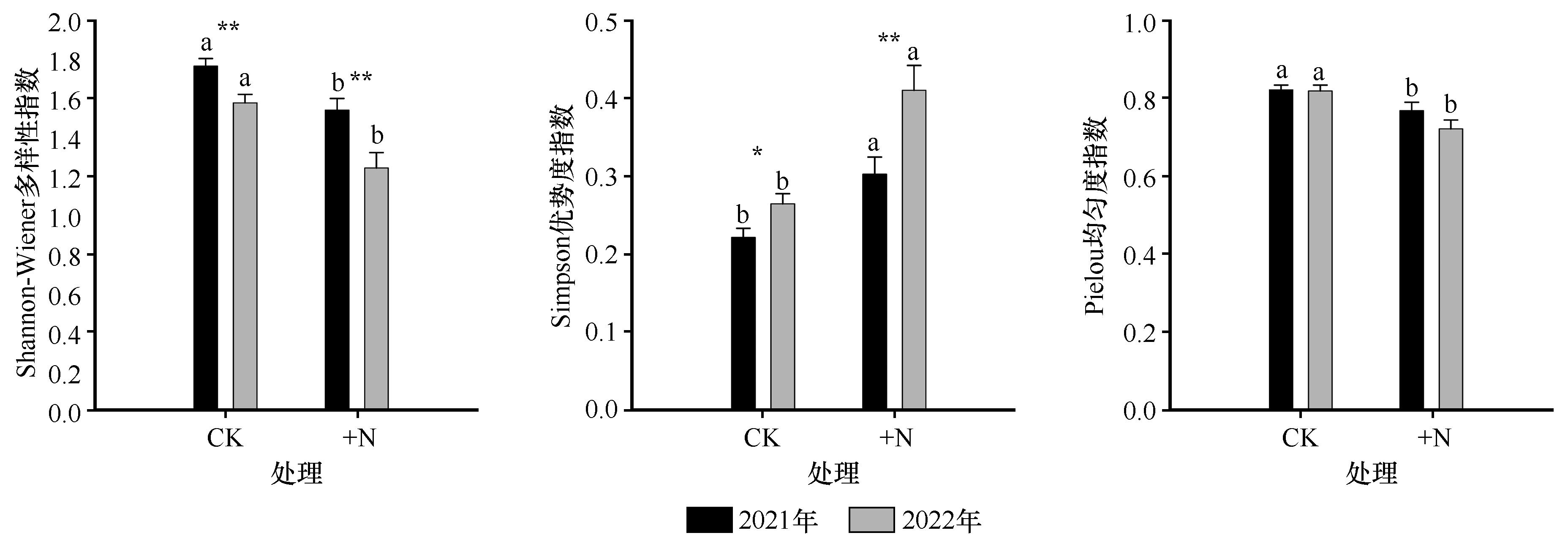
图5 氮添加对沙质草地植被多样性指数的影响注:CK,未添加氮;+N,添加氮素。不同小写字母表示同一年度不同处理间具有显著差异(P<0.05),*表示同一处理下不同年际间具有显著差异(P<0.05),**表示同一处理下不同年际间具有极显著差异(P<0.01)
Fig.5 Effects of nitrogen addition on vegetation diversity indices in sandy grassland
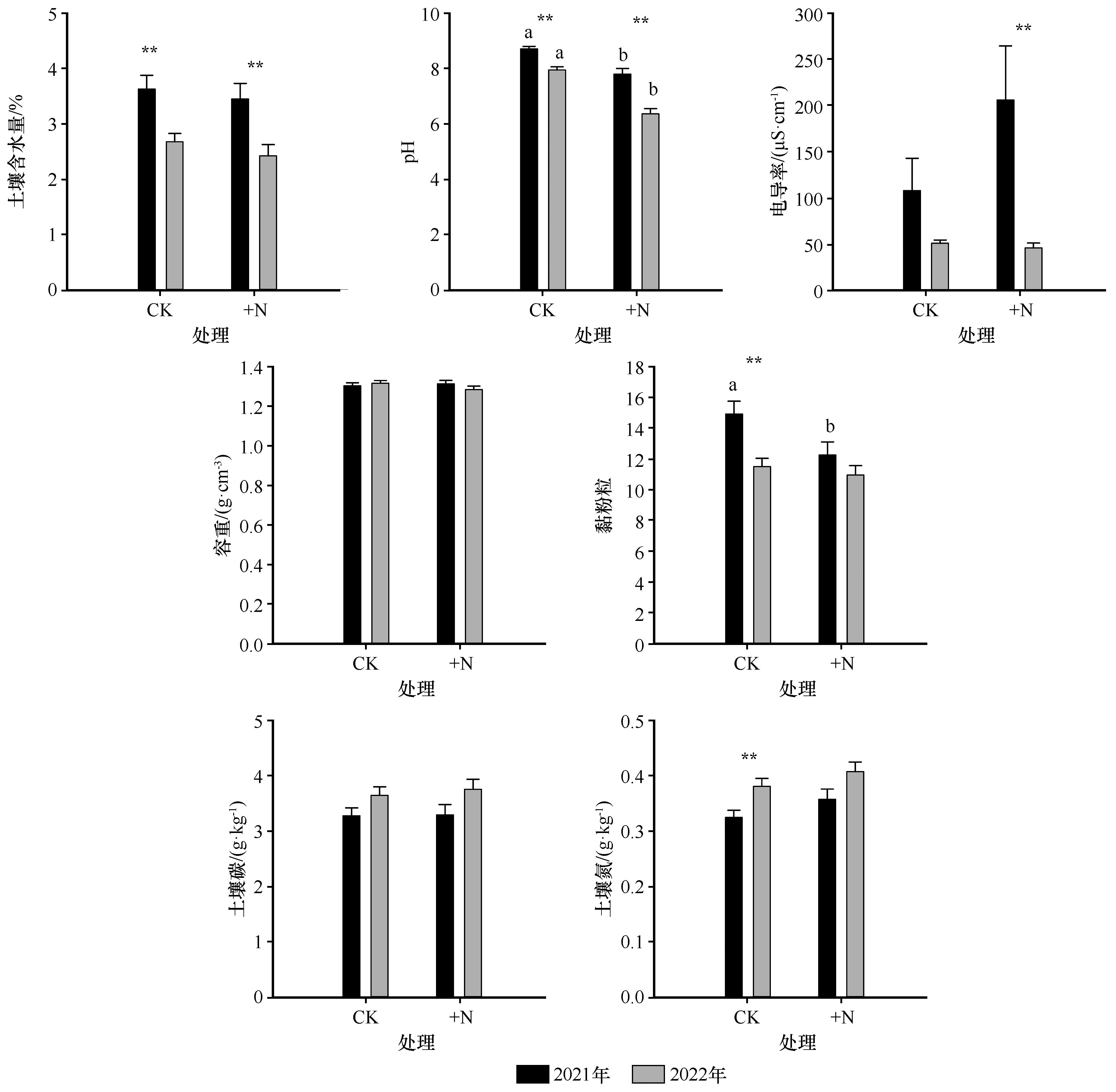
图6 氮添加对沙质草地土壤理化性质的影响注:CK,未添加氮;+N,添加氮素。不同小写字母表示同一年度不同处理间具有显著差异(P<0.05),**表示同一处理下不同年际间具有极显著差异(P<0.01)
Fig.6 Effects of nitrogen addition on soil physicochemical properties in sandy grassland
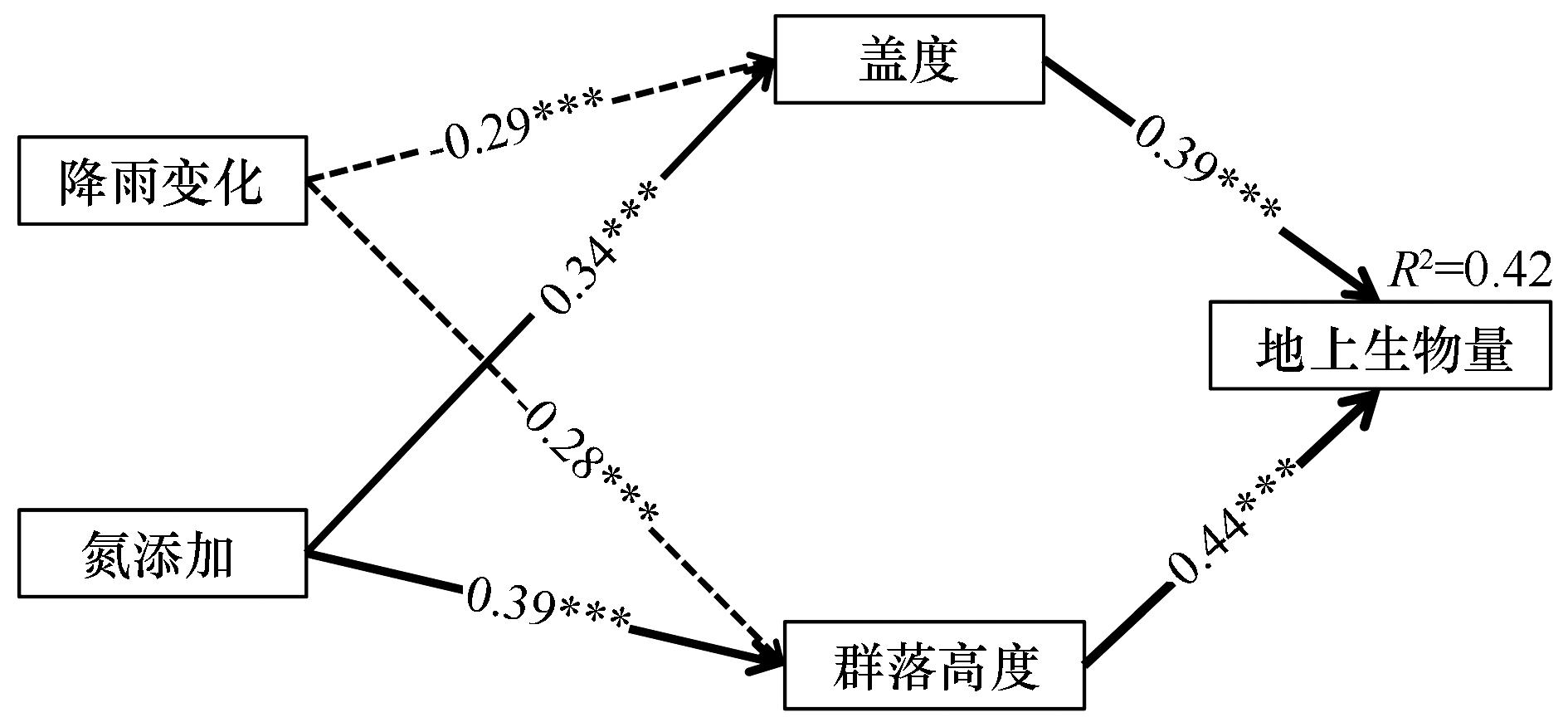
图7 影响沙质草地地上生物量效应路径的结构方程模型注:数字表示标准通径系数,其中实线表示正向影响,虚线表示负向影响,***表示P<0.001
Fig.7 Structural equation model illustrating the effect pathways influencing aboveground biomass in sandy grassland
| [1] | IPCC.AR6 Synthesis Report:Climate Change 2023[R].Cambridge,UK:Cambridge University Press,2023. |
| [2] | Montràs-Janer T, Suggitt A J, Fox R,et al.Anthropogenic climate and land-use change drive short-and long-term biodiversity shifts across taxa[J].Nature Ecology & Evolution,2024,8(4):831-831. |
| [3] | Liu H, Ren F R, Wan S Q,et al.Nitrogen and water additions with or without mowing altered soil microbial community characteristics in a semi-arid steppe[J].Ecological Processes,2025,14(1):3-19. |
| [4] | Gao T, Wang H X J, Zhou T J.Changes of extreme precipitation and nonlinear influence of climate variables over monsoon region in China[J].Atmospheric Research,2017,197:379-389. |
| [5] | 丁一汇.中国的气候变化及其预测[M].北京:气象出版社,2016. |
| [6] | 周波涛,钱进.IPCC AR6报告解读:极端天气气候事件变化[J].气候变化研究进展,2021,17(6):713-718. |
| [7] | 李卓.植物多样性与全球变化因素对松嫩草地土壤多功能性的影响与机制[D].长春:东北师范大学,2022. |
| [8] | Liu X, Zhang Y, Han W,et al.Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China[J].Nature,2013,494(7438):459-462. |
| [9] | Clark C M, Tilman D.Loss of plant species after chronic low-level nitrogen deposition to prairie grasslands[J].Nature,2008,451(7179):712-715. |
| [10] | 周欣,左小安,赵学勇,等.半干旱沙地生境变化对植物地上生物量及其碳、氮储量的影响[J].草业学报,2014,23(6):36-44. |
| [11] | 张腊梅,刘新平,赵学勇,等.科尔沁固定沙地植被特征对降雨变化的响应[J].生态学报,2014,34(10):2737-2745. |
| [12] | Zhou J, Fu B J, Gao G Y,et al.Effects of precipitation and restoration vegetation on soil erosion in a semi-arid environment in the Loess Plateau,China[J].Catena,2016,137:1-11. |
| [13] | 姜基春,王国强,郭宁,等.黄土高原4种植被带草本群落特征及其对降水变化的响应[J].西北植物学报,2019,39(10):1861-1867. |
| [14] | 吴珂,徐文轩,杨维康.模拟短期降雨量变化对准噶尔荒漠植物群落的影响[J].水土保持研究,2019,26(5):100-106. |
| [15] | Han Y H, Dong S K, Zhao Z Z,et al.Response of soil nutrients and stoichiometry to elevated nitrogen deposition in alpine grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J].Geoderma,2019,343:263-268. |
| [16] | Liu X C, Shi X M, Zhang S T.Soil abiotic properties and plant functional diversity co-regulate the impacts of nitrogen addition on ecosystem multifunctionality in an alpine meadow[J].Science of the Total Environment,2021,780:146476. |
| [17] | Shi J B, Rahman M K U, Ma R N,et al.Effects of nitrogen enrichment on soil enzyme activities in grassland ecosystems in China:a multilevel meta-analysis[J].Pedosphere,2025,35(1):84-96. |
| [18] | Harpole W S, Sullivan L L, Lind E M,et al.Addition of multiple limiting resources reduces grassland diversity[J].Nature,2016,537:93-96. |
| [19] | Zhou W X, Li C J, Fu B J,et al.Changes and drivers of vegetation productivity in China's drylands under climate change[J].Environmental Research Letters,2024,19(11):114001. |
| [20] | 李元恒.内蒙古荒漠草原植物群落结构和功能对增温和氮素添加的响应[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2014. |
| [21] | Liu X, Duan L, Mo J,et al.Nitrogen deposition and its ecological impact in China:an overview[J].Environmental Pollution,2011,159(10):2251-2264. |
| [22] | Yuan X B, Niu D C, Gherardi L A,et al.Linkages of stoichiometric imbalances to soil microbial respiration with increasing nitrogen addition:evidence from a long-term grassland experiment[J].Soil Biology & Biochemistry,2019,138:107580. |
| [23] | 贺星.养分添加对内蒙古草原生物量和多样性的影响[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古大学,2014. |
| [24] | 辛小娟.氮、磷添加对亚高山草甸地上/地下生物量分配及植物功能群组成的影响[D].兰州:兰州大学,2011. |
| [25] | 张继义,赵哈林,张铜会,等.科尔沁沙地植被恢复系列上群落演替与物种多样性的恢复动态[J].植物生态学报,2004,28(1):86-92. |
| [26] | Lv P, Sun S S, Li Y Q,et al.Plant composition change mediates climate drought,nitrogen addition,and grazing effects on soil net nitrogen mineralization in a semi-arid grassland in North China[J].Science of the Total Environment,2024,908. |
| [27] | 张晶,左小安.沙质草地植物功能性状对放牧,增水,氮添加及其耦合效应的响应机制[J].生态学报,2021,41(18):7153-7167. |
| [28] | 张丽芳,胡海林.土壤酸碱性对植物生长影响的研究进展[J].贵州农业科学,2020,48 (8):40-43. |
| [29] | Cao W J, Li Y Q, Chen Y,et al.Spatial patterns of soil stoichiometry and their responses to land use in a desertified area:a case study of China's Horqin Sandy Land[J].Land Degradation & Development,2024,35(1):350-359. |
| [30] | 孙一梅,田青,郭爱霞,等.水、氮施用量对科尔沁沙地植被特征和叶性状的影响[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(6):223-232. |
| [31] | 周欣,左小安,赵学勇,等.科尔沁沙地中南部34种植物叶功能性状及其相互关系[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(6):1489-1495. |
| [32] | 王明明,刘新平,何玉惠,等.科尔沁沙质草地生物量积累过程对降水变化的响应模拟[J].生态学报,2020,40(11):3656-3665. |
| [33] | 周欣扬.降水变化对典型草原土壤特征及植物群落结构的影响[D].银川:宁夏大学,2023. |
| [34] | 许艺馨.降水量对荒漠草原土壤呼吸的影响机制研究[D].银川:宁夏大学,2022. |
| [35] | 李晓辉.沙质草地植物群落特征和土壤质量对氮磷养分添加的响应[D].兰州:兰州交通大学,2021. |
| [36] | 张蕊,赵学勇,李刚,等.干旱半干旱区草地植物-土壤响应降水和管理措施的研究综述[J].中国沙漠,2025,45(1):131-140. |
| [37] | Bai Y F, Wu J G, Clark C M,et al.Tradeoffs and thresholds in the effects of nitrogen addition on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning:evidence from Inner Mongolia Grasslands[J].Global Change Biology,2010,16(1):358-372. |
| [38] | 张彦东,沈有信,刘文耀.金沙江干旱河谷退化草地群落对氮磷施肥的反应[J].植物研究,2004,24(1):59-64. |
| [39] | Wang J F, Knops J M H, Brassil C E,et al.Increased productivity in wet years drives a decline in ecosystem stability with nitrogen additions in arid grasslands [J].Ecology,2017,98(7):1779-1786. |
| [40] | 杨倩,王娓,曾辉.氮添加对内蒙古退化草地植物群落多样性和生物量的影响[J].植物生态学报,2018,42(4):430-441 |
| [41] | 徐锰瑶,李雪华,刘思洋,等.围封和水氮添加对重度退化草地植物多样性的影响[J].生态环境学报,2020,29(9):1730-1737. |
| [42] | Zhang J, Zuo X A, Zhao X Y,et al.Effects of rainfall manipulation and nitrogen addition on plant biomass allocation in a semiarid sandy grassland[J].Scientific Reports,2020,10:9026. |
| [43] | 詹瑾,丛安琪,李玉霖,等.长期氮沉降和地上凋落物处理对半干旱区沙质草地表层土壤碳氮组分的影响[J].水土保持学报,2023,37(4):227-234. |
| [44] | 吴传敬,张雨雪,肖杨,等.气候和植被影响土壤理化性质及微生物对氮添加的响应全球控制实验Meta分析[J].生态学报,2025,45(5):2152-2161. |
| [45] | 肖胜生.温带半干旱草地生态系统碳固定及土壤有机碳库对外源氮输入的响应[D].北京:中国科学院,2010. |
| [46] | Thomey M L, Collins S L, Vargas R,et al.Effect of precipita tion variability on net primary production and soil respiration in a Chihuahuan Desert grassland[J].Global Change Biology,2011,17(4):1505-1515. |
| [47] | 何毅.水氮添加对毛乌素沙地柠条固沙区草本层植被和土壤特征的影响[D].银川:宁夏大学,2022. |
| [48] | Delgado-Baquerizo M, Maestre F T, Reich P B,et al.Microbial diversity drives multifunctionality in terrestrial ecosystems[J].Nature Communications,2016,7:10541. |
| [49] | Chen W Q, Wang J Y, Chen X,et al.Soil microbial network complexity predicts ecosystem function along elevation gradients on the Tibetan Plateau[J].Soil Biology & Biochemistry,2022,172:108766. |
| [50] | Lv P, Sun S S, Li Y Q,et al.Growing-season drought and nitrogen addition interactively impair grassland ecosystem stability by reducing species diversity,asynchrony,and stability[J].Science of the Total Environment,2023,912:169122. |
| [1] | 姚博, 连杰, 龚相文, 牟晓明, 李玉霖, 李玉强, 王旭洋. 科尔沁沙地土壤微生物碳氮磷化学计量空间格局及影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 153-165. |
| [2] | 景家琪, 刘新平, 何玉惠, 丰洁, 胡鸿姣, 徐远志. 半干旱沙质草地植物群落构建对降水的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 314-323. |
| [3] | 景家琪, 刘新平, 何玉惠, 丰洁, 胡鸿姣, 徐远志, 张尧. 降水量对半干旱沙质草地土壤胞外酶活性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 368-377. |
| [4] | 丁甲, 唐逸云, 李蕾, 杨宏玉, 张泽琦, 王君, 余舒畅, 冯金朝, 石莎, 杨昊天. 土壤水分与氮含量对宁夏荒漠草原甘肃蒿( Artemisia gansuensis )、胡枝子( Lespedeza bicolor )、针茅( Stipa capillata )生理的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(3): 271-282. |
| [5] | 李玉倩, 王旭洋, 林宏东, 牟晓明, 刘伟媛, 连杰, 李玉强. 海拔对马衔山生态系统土壤-微生物碳氮磷计量特征的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(1): 151-161. |
| [6] | 鲍莉莉, 李锦荣, 韩兆恩, 刘悦, 单浩东. 基于无人机多源数据的梭梭( Holoxylon ammodendron )地上生物量估算[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 50-59. |
| [7] | 李成阳, 黄樱宜, 林千策, 沈琳丽, 罗诗影, 梁志辉, 李臻明, 彭飞, 薛娴. 长江源区高寒草甸生长季载畜量对模拟增温的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 165-173. |
| [8] | 包天玲, 刘继亮, 苑峰, 李寅龙, 贾振宇, 潘成臣. 科尔沁沙质草地植物群落对增温的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 151-160. |
| [9] | 张晶, 左小安, 吕朋. 土壤水分和养分对沙质草地优势植物叶片氮回收效率的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 161-169. |
| [10] | 甘开元, 张金霞, 陈丽娟, 席海洋, 张斌武, 雍天, 卫雨西. 乌兰布和沙漠沿黄河段植物群落特征及空间分异[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 180-190. |
| [11] | 焦冰洁, 张丙昌, 赵康, 闫丽霞, 武志芳. 生物结皮演替对黄土高原水蚀风蚀交错区土壤氮素转化及微生物活性的促进效应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 191-199. |
| [12] | 王培源, 杨昊天, 张雪, 刘秉青, 李云飞, 蒋齐, 王占军, 吴旭东, 刘立超. 蒙古冰草(Agropyron mongolicum var. mongolicum)构件生物量分配特征对土壤类型的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 74-84. |
| [13] | 翟军团, 陈向向, 李秀, 张山河, 韩晓莉, 李志军. 胡杨( Populus euphratica )枝叶异速生长关系随发育阶段及冠层高度变化的性别差异[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 116-127. |
| [14] | 李小乐, 党晓宏, 翟波, 魏亚娟, 迟旭, 吴惠敏. 白刺( Nitraria tangutorum )灌丛不定根构型特征及生物量分配模式[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 172-180. |
| [15] | 王怀海, 黄文达, 何远政, 牛亚毅, 朱远忠. 短期增温和降水减少对沙质草地土壤微生物量碳氮和酶活性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(3): 274-281. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
